Nursing Home Costs, Care Options, and Funding Guide for Elder Care in US 2025
As the population ages, understanding nursing home care becomes increasingly important for many American families. This comprehensive guide explores the costs, care options, and funding strategies for nursing home care in the United States, with a focus on the landscape expected in 2025.
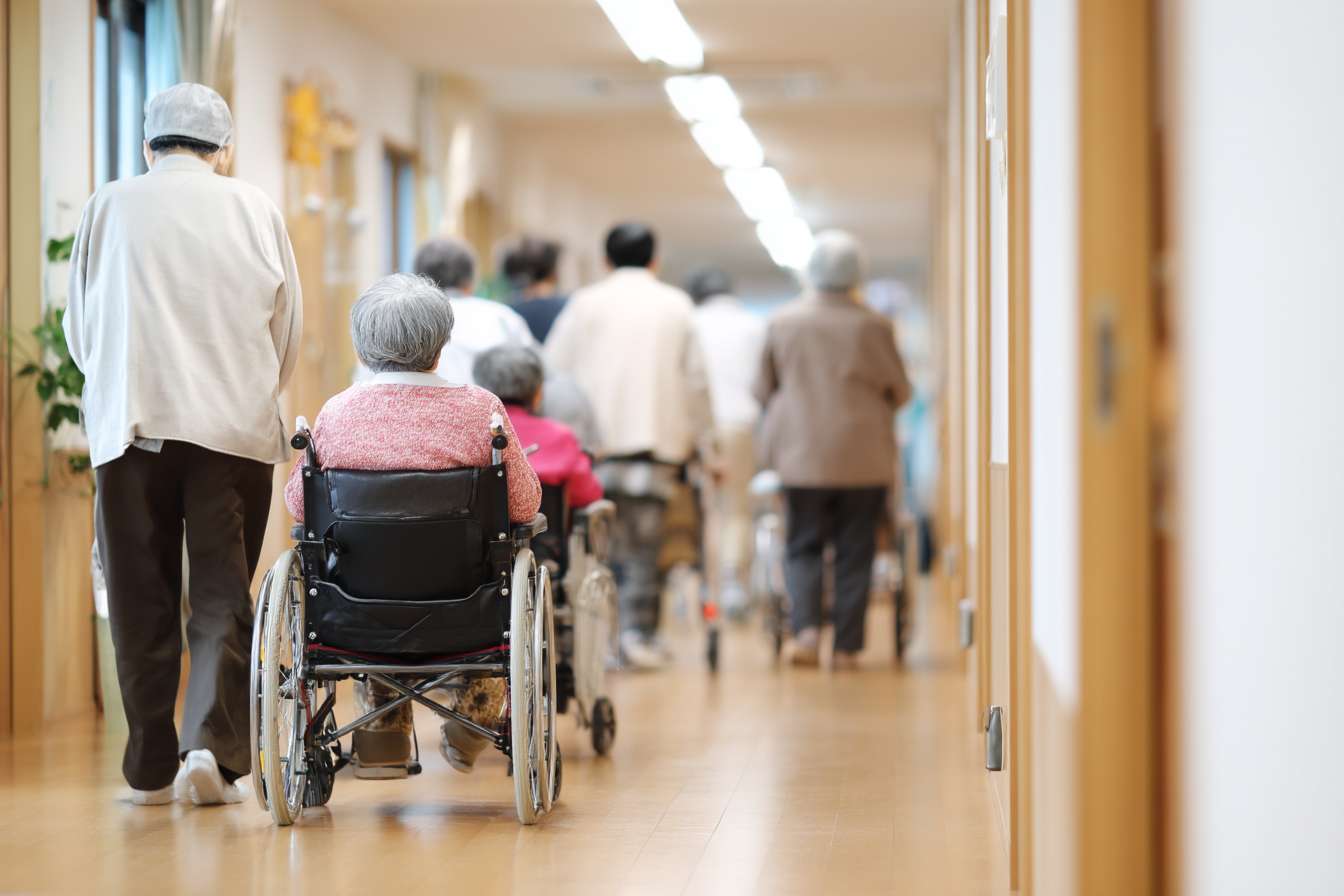

What are the typical nursing home costs in 2025?
Nursing home costs in the United States vary widely depending on factors such as location, level of care required, and facility amenities. In 2025, the average annual cost for a private room in a nursing home is projected to be approximately $120,000, while a semi-private room may cost around $105,000 per year. These figures represent a significant financial commitment for most families.
It’s important to note that costs can differ substantially between urban and rural areas, with major metropolitan centers often commanding higher prices. Additionally, specialized care for conditions like Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia may incur additional expenses.
How can one determine eligibility for nursing home support?
Eligibility for nursing home support often depends on both financial and medical criteria. Medicaid, the primary source of nursing home funding for many Americans, typically requires that individuals have limited income and assets. In 2025, most states are expected to have an asset limit of around $2,000 for an individual, though this may vary.
Medical eligibility is generally determined by a comprehensive assessment of an individual’s ability to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) independently. This evaluation considers factors such as mobility, hygiene, and cognitive function. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or social worker to understand specific eligibility requirements, as they can change over time and vary by state.
What nursing home care options are available?
Nursing homes offer a range of care options to meet diverse needs:
-
Skilled Nursing Care: Provides 24-hour medical supervision and assistance with ADLs.
-
Memory Care: Specialized units for individuals with Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia.
-
Rehabilitation Services: Short-term care for those recovering from surgery or illness.
-
Respite Care: Temporary care to provide relief for primary caregivers.
-
Hospice Care: End-of-life care focusing on comfort and quality of life.
Some facilities may offer all of these services, while others specialize in specific types of care. It’s crucial to assess individual needs and preferences when selecting a nursing home care option.
How can one fund nursing home care for elders in the US?
Funding nursing home care often requires a combination of strategies:
-
Long-Term Care Insurance: Policies specifically designed to cover nursing home costs.
-
Medicaid: Government program for those with limited financial resources.
-
Medicare: Covers short-term skilled nursing care under certain conditions.
-
Veterans Benefits: VA Aid and Attendance program for eligible veterans and their spouses.
-
Personal Savings and Assets: Using retirement accounts, investments, or selling property.
-
Reverse Mortgages: Allow homeowners to access home equity for care costs.
| Funding Option | Eligibility | Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| Medicaid | Low-income individuals | Long-term care costs |
| Medicare | 65+ or certain disabilities | Short-term skilled nursing (up to 100 days) |
| Long-Term Care Insurance | Varies by policy | Depends on policy terms |
| Veterans Benefits | Eligible veterans and spouses | Partial coverage for long-term care |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
What factors should be considered when choosing a nursing home for elder care?
When selecting a nursing home for elder care, consider the following:
-
Quality of Care: Review state inspection reports and Medicare’s Nursing Home Compare tool.
-
Staff-to-Resident Ratio: Higher ratios often indicate better care.
-
Facility Cleanliness and Safety: Visit in person to assess conditions.
-
Activities and Social Engagement: Look for programs that match the elder’s interests.
-
Proximity to Family: Consider how often loved ones can visit.
-
Specialized Care Offerings: Ensure the facility can meet specific medical needs.
-
Cultural and Dietary Considerations: Check if the facility accommodates personal preferences.
It’s recommended to visit multiple facilities, speak with staff and residents, and carefully review contracts before making a decision.
As we look towards 2025, the landscape of nursing home care continues to evolve. While costs remain a significant concern for many families, understanding the available options and funding strategies can help in planning for quality elder care. By carefully considering individual needs, exploring various care options, and leveraging appropriate funding sources, families can make informed decisions to ensure the best possible care for their loved ones in their later years.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.