A Guide to Industrial Fittings and Their Applications
Industrial fittings serve as critical components in manufacturing systems, connecting pipes, tubes, and equipment to ensure safe and efficient fluid flow. These mechanical joints handle everything from water and chemicals to gases and steam across diverse industrial environments. Understanding their functions, materials, and proper selection criteria helps engineers and technicians maintain reliable operations while meeting safety standards and regulatory requirements.
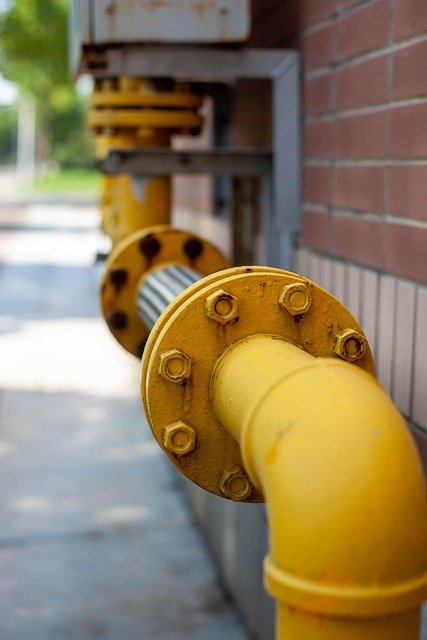

Industrial fittings form the backbone of manufacturing infrastructure, enabling secure connections between pipes, tubes, hoses, and equipment. These components facilitate the controlled movement of liquids, gases, and other materials throughout industrial processes, from chemical plants to food processing facilities.
What Industrial Fittings Do: Functions Types and Standards
Industrial fittings serve multiple essential functions in manufacturing environments. They create leak-proof connections between different pipe sections, change flow directions through elbows and tees, reduce or increase pipe diameters using reducers, and provide access points for maintenance through unions and flanges. Common fitting types include straight couplings for joining pipes of equal diameter, elbows for directional changes, tees for branching connections, and reducers for size transitions.
Industry standards govern fitting specifications to ensure compatibility and safety. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) establishes dimensional requirements, while the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) sets pressure and temperature ratings. International standards like ISO 4144 provide global compatibility guidelines for hydraulic fittings.
Materials and Coatings: Corrosion Temperature and Compatibility
Material selection directly impacts fitting performance and longevity. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and handles high temperatures, making it suitable for chemical processing and food applications. Carbon steel provides strength and cost-effectiveness for general industrial use but requires protective coatings in corrosive environments. Brass fittings work well with water systems and offer good machinability, while plastic materials like PVC and CPVC handle corrosive chemicals at moderate temperatures.
Coatings enhance fitting durability and performance. Zinc plating provides basic corrosion protection for steel fittings, while nickel plating offers superior resistance to chemicals and wear. Specialized coatings like PTFE (Teflon) create non-stick surfaces for food processing applications, and epoxy coatings protect against harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures.
Sizing and Selection: Pressure Flow Threads and Sealing
Proper fitting selection requires careful consideration of system parameters. Pressure ratings must exceed maximum operating pressure with appropriate safety factors, typically 4:1 for static applications. Flow capacity depends on fitting internal diameter and configuration, with sharp bends and restrictions reducing flow rates. Thread compatibility ensures secure connections, with National Pipe Thread (NPT) being common in North America and British Standard Pipe (BSP) used internationally.
Sealing methods vary based on application requirements. Tapered threads create mechanical seals through interference fit, while parallel threads require separate sealing elements like O-rings or gaskets. Metal-to-metal seals handle high pressures and temperatures, while elastomeric seals provide flexibility and easier assembly.
| Fitting Type | Material Options | Pressure Range (PSI) | Temperature Range (°F) | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded Couplings | Stainless Steel, Brass, Carbon Steel | 150-6000 | -20 to 800 | $5-50 per piece |
| Compression Fittings | Brass, Stainless Steel, Plastic | 200-3000 | -40 to 400 | $8-75 per piece |
| Flanged Connections | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | 150-2500 | -20 to 1000 | $25-300 per set |
| Quick Disconnect | Stainless Steel, Brass | 250-5000 | -10 to 300 | $15-150 per pair |
| Welded Fittings | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | 300-10000 | -50 to 1200 | $10-200 per piece |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Installation Testing and Maintenance: Doing It Right and Keeping It Tight
Proper installation ensures fitting reliability and system safety. Thread preparation involves cleaning and applying appropriate sealants or tape, with pipe dope or PTFE tape being common choices. Tightening torque must follow manufacturer specifications to prevent over-tightening that damages threads or under-tightening that causes leaks. Alignment verification ensures stress-free connections that won’t fail under thermal expansion or vibration.
Testing procedures validate installation quality and system integrity. Pressure testing typically involves applying 1.5 times operating pressure for specified durations, with visual inspection for leaks or deformation. Leak detection methods include soap bubble testing for gas systems and dye penetrant testing for critical applications. Documentation of test results provides maintenance baselines and regulatory compliance records.
Regular maintenance extends fitting life and prevents costly failures. Visual inspections identify corrosion, wear, or damage before problems escalate. Torque verification ensures connections remain tight despite thermal cycling and vibration. Replacement schedules based on service conditions and manufacturer recommendations prevent unexpected failures in critical systems.
Industrial fittings represent essential components that require careful selection, proper installation, and regular maintenance to ensure safe and efficient operations. Understanding their functions, materials, and application requirements enables informed decisions that optimize system performance while maintaining safety standards across diverse industrial environments.